Introduction
Not every varicose vein is the same, and neither are its causes and symptoms. Knowing the different types of varicose veins is crucial so that you can take proactive measures towards the treatment of varicose vein disease at an early stage, when it is referred to as spider veins This article will provide you with all the relevant information about different kinds of varicose veins, their causes and the best surgical options.
Understanding The Different Types Of Varicose Veins
Are you experiencing discomfort and embarrassment due to varicose veins? These larger, swollen, or brightly colored veins can form anywhere on the body, although they usually start on the lower legs. Different types of varicose veins include-
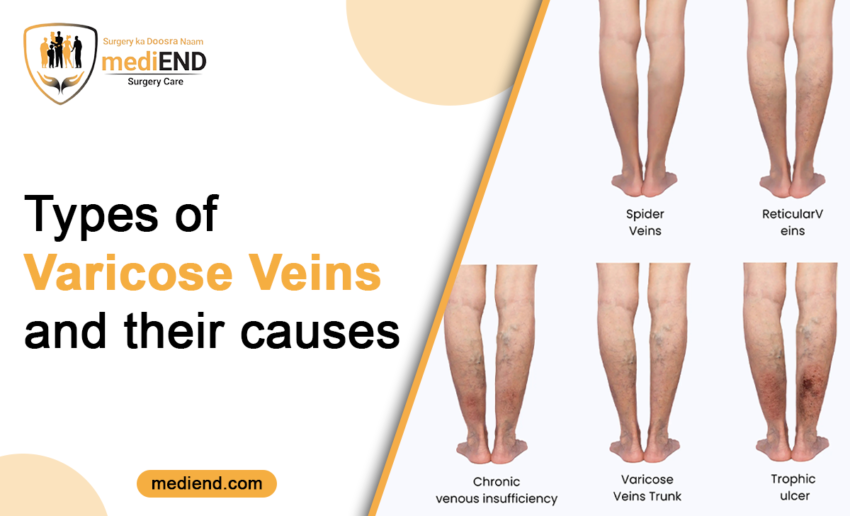
1. Telangiectasia varicose veins
- “Spider veins” is the term used to describe this type of varicose vein.
- They have a red, blue, or purple color and a tendency to spread out in a webbed pattern. They develop on the face in addition to the legs and ankles.
- They appear on the skin as a network of lines resembling a spider’s web due to the expansion of venules, the blood vessels that are closest to the skin.
- Rarely, they may be brought on by dangerous illnesses such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). This is the situation where telangiectasia occurs on the important organs as opposed to under the skin.
- Symptoms include- recurring nosebleeds, breathlessness, stool containing blood, minor strokes and seizures.
2. Reticular varicose veins
- Reticular veins are noticeable, brightly colored varicose veins that are neither elevated nor rope-like.
- They are frequently blue or purple in color and usually thicker than spider veins. Compared to telangiectasia varicose veins, this type of varicose vein covers a larger surface area and stretches out like a mesh.
- They develop on the backs of the knees, on the inner thighs, or close to the ankles.
- The main cause of these varicose veins is vascular insufficiency, a disorder in which the valves cannot pump blood to the heart and blood accumulates inside of them.
- Although almost anyone can develop these types of varicose veins, you are more vulnerable if:
– You spend a lot of time sitting or standing stationary,
– You have varicose veins in your family.
– You’re expecting a child.
– You are either obese or overweight.
3. Saphenous varicose veins
- Leg saphenous veins are impacted by this type of varicose veins, sometimes referred to as “trunk” varicose veins.
- It is the primary superficial vein linked to varicose veins. From the ankle to the groin, it is a continuous swelling.
- When the valves of this vein malfunctions, blood collects or runs back toward the ankle. This can cause the veins to become deformed and give the appearance of being very enlarged, pushing through the skin.
- Occasionally, aching, itching, cramping, soreness, and discomfort can result from sapphire varicose veins. If left untreated, saphenous varicose vein problems can cause bleeding, ulceration, and skin abnormalities, including varicose eczema.
- The same variables that cause reticular and telangiectasia varicose veins also typically cause saphenous varicose veins. Although they can affect anyone, you run a higher risk if-
– You lead a sedentary lifestyle, sitting or standing for the majority of the day.
– You are either obese or overweight.
– You possess a family history of vein varicosities.
– You are pregnant.
4. Perforating Varicose Veins
- The abnormal, enlarged veins known as perforating varicose veins develop when the tiny capillaries that connect the deep veins to the superficial veins stop functioning properly.
- This incapacity causes the superficial veins to press harder and flow blood backward, or reflux, which makes the veins appear to be bulging.
- Valves that are weak or breakable might generate reflux, which can cause blood to pool in the superficial veins.
- The risk of perforating varicose veins can be raised by the following conditions-
– A family history of vein problems.
– Obesity, extended standing, and pregnancy are some of the conditions that might increase venous system pressure and cause valve failure.
– Vein flexibility and strength can decrease with age, which raises the possibility of valve incompetence.
– Inadequate physical exercise, smoking, and sedentary behaviour can all make vein problems worse.
Varicose Veins Symptoms, Causes and Treatments
What are the Different Surgical Treatments For Varicose Veins?
Vein Stripping: A conventional surgical technique that entails making tiny skin incisions to remove the damaged vein.
Method-
- Anesthesia: Usually administered under a combination of local anesthetic and sedation, or general anesthesia.
- Incisions: The afflicted vein is incised at both ends, usually in the groin and behind the knee during this type of varicose vein surgery.
- Vein Removal: A specialized tool is inserted into the vein in order to remove the vein entirely. There are instances where vein segments may need to be removed.
- Closure: Adhesive or sutures are used to seal the incisions.
Recovery-
- It could take a few weeks for patients to fully recover.
- Although common, swelling, bruising, and discomfort can be controlled with medicine.
Endovenous laser ablation: A less invasive method of sealing varicose veins with laser energy.
Method-
- Anesthesia: The treatment region is covered with a local anesthetic.
- Insertion: A tiny incision is made, and a thin laser fiber is introduced into the injured vein.
- Application of the Laser: When the laser is turned on, heat-producing radiation is released into the veins, causing the walls to collapse and close.
- Closure: A compression bandage is placed once the fiber is cut out.
- recuperation
Recovery-
- After 1-2 days, the majority of patients return to their regular activities.
- Bristles and some irritation are possible, although they usually go away fast.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy: A minimally invasive technique for eliminating varicose veins near the skin’s surface.
Method-
- Anesthesia: To make the area numb, local anesthetic is applied.
- Vein Removal: The doctor makes tiny incisions and uses a hook-like instrument to remove the veins.
Recovery-
- Very short recovery period- most patients go back to normal activities in a matter of days.
Advantages of Varicose Treatment Through Surgery
Relieving Symptoms: Leg pain, edema, weight, and discomfort can be relieved through different surgical procedures.
Enhanced Visual Appearance: The obvious symptoms of varicose veins can be greatly reduced or eliminated with surgery, improving the legs’ overall appearance.
Avoidance of Adverse Cases: Through Varicose Veins Treatment, possible side effects such skin ulcers, blood clots, and chronic venous insufficiency can be avoided.
Minimally Invasive Choices: Compared to traditional surgery, many minimally invasive current surgical methods such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) have quicker recovery durations.
Rapid Recuperation: Minimally invasive procedures frequently result in quicker recovery times for patients, enabling them to resume regular activities sooner.
Prolonged Outcomes: Long-lasting outcomes from surgical procedures are possible, particularly if patients adhere to lifestyle and post-operative care guidelines.
Risk Factors In Varicose Treatment Through Surgery
Infection: There is always a chance that the incision sites might become infected after surgery.
Bruising and Bleeding: Bruising and bleeding after surgery are common, particularly after invasive operations.
Nerve Injury: A minor chance of nerve injury could cause tingling or numbness in the area that is being treated.
Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can become more likely after surgery, particularly if individuals do not get adequate exercise while recovering.
Recurrence: If underlying risk factors (such as obesity or extended standing) are not addressed after surgery, varicose vein disease may return.
Scarring: Although scars from minimally invasive procedures are usually less obvious, incisions nevertheless have the potential to leave scars.
Adverse effects of anesthesia: Both general anesthesia and local anesthesia carry hazards, just like any other procedure involving anesthesia.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that can affect individuals in various ways, manifesting in several distinct types ranging from trunk varicose veins and reticular veins to spider veins and perforating veins. Understanding the different types of varicose veins is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Although it is possible to prevent varicose veins through lifestyle changes, they do not guarantee complete protection from varicose veins. Early diagnosis is the key to an effective surgical treatment for varicose veins. There are various kinds of surgical procedures designed to treat different types of varicose. Therefore, you must talk to a medical professional for selecting the best course of treatment.
Reach out to us on LinkedIn